X-ray
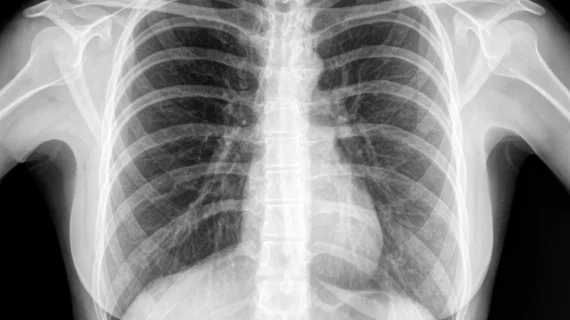
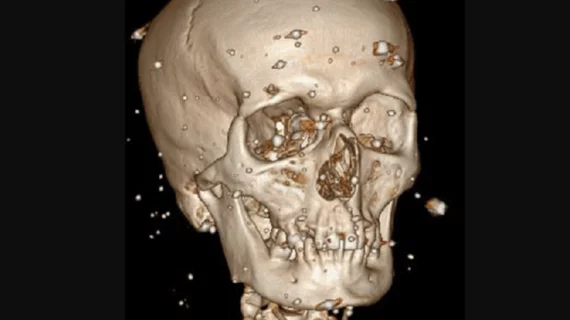
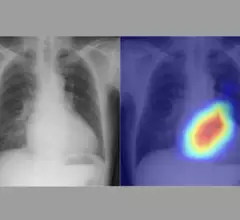
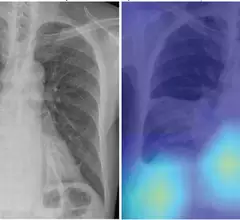
Medical X-rays have mostly converted from film, to computed radiography (CR) that used individual plates to record each X-ray digitally that then had to be uploaded into a PACS, to what is the standard-of-care today with digital radiography (DR). DR X-ray which allows immediate digital transfer of images into a PACS for immediate review. X-rays are used to diagnose fractures, bone abnormalities, lung pathologies and tumors, as well as monitor pediatric growth, plan for surgery and treat oncology patients during radiation therapy. More detailed anatomical imaging, especially soft tissue imaging, is usually sent for advanced imaging with CT or MRI. X-ray, especially mobile DR systems, are a primary use case for artificial intelligence (AI) integration.