Lung scarring occurs in up to 11% of patients recovered from COVID, regardless of infection severity
Researchers recently estimated that up to 11% of patients who recover from COVID could have lung scarring that may worsen over time.
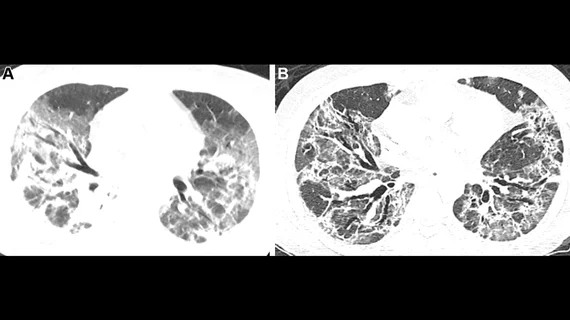
This data was published recently in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, where experts used the follow-up CT imaging (completed within 240 days of discharge) from 209 patients hospitalized with COVID to stratify the risk of residual lung damage for a post-hospitalization cohort of almost 3,500 individuals without follow-up imaging.
Corresponding author Iain Stewart, PhD, of the Margaret Turner Warwick Center for Fibrosing Lung Disease and co-authors suggested that the team’s work could have major implications for patients who are released from the hospital following a COVID infection, as a “substantial” number of these individuals could have fibrotic abnormalities of the lungs that need to be addressed and potentially managed.
“For some people these fibrotic patterns may be stable or resolve, while for others they may lead to longer term lung fibrosis progression, worse quality of life and decreased life expectancy,” the authors wrote. “Earlier detection of progression is essential to improving outcomes.”
The findings revealed that although patients with the most severe cases of COVID (those requiring ventilation, etc.) were more likely to display residual lung abnormalities indicative of interstitial lung disease following their release, nearly 8% of patients with less severe cases were also found to be at high risk.
The researchers acknowledged that they cannot yet determine whether these changes will progress or resolve in the long-term, but they have planned a second phase of research that will reevaluate study participants at the 12-month mark.
“At that time, we will also use linked electronic health records of hospital admissions and mortality data to support our analyses. We expect to have the final results in early 2023,” the authors stated.
To learn more, click here.