These CT findings increase risk of thromboembolic events for patients with COVID pneumonia
New research highlights key CT findings that radiologists should be aware of when interpreting the exams of patients with COVID pneumonia.
The paper details an analysis of 276 COVID patients and how their image findings correlated to their experiences with thromboembolic events. Corresponding author of the paper Mohd Ghadeeb, MD, from the Radiology Department at King Fahad Hospital in Saudi Arabia, and colleagues explained the importance and challenges involved in understanding COVID patients’ risks of clotting complications recently in Cureus:
“Thromboembolic manifestations have a wide spectrum and vary significantly among different patients. These include venous thromboembolic events, arterial events, and microvascular thrombosis,” the researchers wrote. “The diagnosis of venous thromboembolic events, including deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, can be challenging due to overlapping clinical and laboratory features.”
Ghadeeb and colleagues looked at the chest CT scans of patients admitted to their hospital with COVID pneumonia while also reviewing the patients’ electronic health records to single out anyone who had experienced a thromboembolic event. Out of these 276 admitted patients, 64 experienced thromboembolic events, 51 of whom were diagnosed with pulmonary embolism and 16 with deep vein thrombosis.
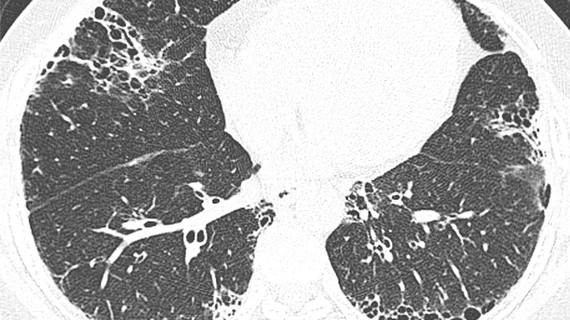
Patients aged 51 to 65 or older than 65 were found to have increased risks for complications. In addition, the authors observed the following associations between image findings and thromboembolic events:
Crazy-paving appearance of opacity
Severe pulmonary parenchymal involvement of opacities
The authors noted that radiologists should be highly suspicious of pulmonary embolism and DVT when they encounter these findings on chest CT exams of COVID patients, suggesting that doing so could detect such complications in their earliest manifestations.
The full study can be viewed for free here.