4D flow MRI has potential role for detecting complications in patients with aortic disease
Four-dimensional cardiac MRI can pinpoint patients with a higher risk of deadly complications from aortic degeneration, according to recent research out of Northwestern University.
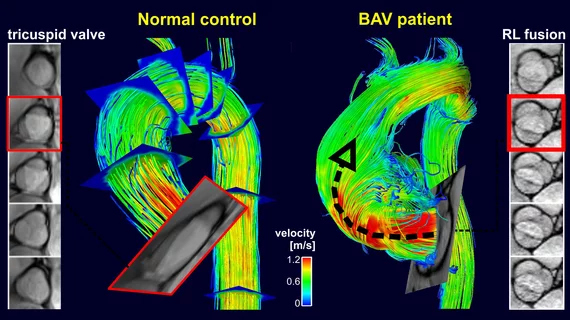
Aorta wall shear stress occurs when blood flow exerts force against the arterial wall in the heart. 4D flow MRI can quantify areas exposed to high stress levels but experts sought to determine if this information could be used to detect aortic disease associated with severe complications, including rupture and ascending aorta aneurysm.
After following more than 70 participants for at least five years, the group reported positive results in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
“Our findings indicate a potential role of 4D flow MRI-derived wall shear stress as a new biomarker for arterial wall remodeling leading to higher rates of progressive aortic dilation in bicuspid aortic valve disease, thus exposing patients to a greater risk for aortic complications,” Michael Markl, PhD, professor and vice chair for research at Northwestern’s Departments of Radiology & Biomedical Engineering said Thursday.
For their study, Markl and colleagues studied 72 patients assigned to MRI surveillance for potential aortic dilation at baseline and five-year follow-up. Those with higher rates of dilation showed elevated shear stress levels during their initial appointments (19.9%) compared to patients with slower aortic growth rates (5.7%).
“I think this a landmark paper for our group,” S. Christopher Malaisrie, MD, a cardiothoracic surgeon at Northwestern Medicine’s Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute, said in a statement. “It proves our concept that wall shear stress has a downstream effect on aortic degeneration. We’re a step closer to using 4D MRI for clinical decision making.”