Prostate ablation AI 'contouring assistant' lands FDA clearance
An artificial intelligence “contouring assistant” that can be used to guide precision ultrasound ablation procedures of the prostate has just earned the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s 510(k) clearance.
Canada-based Profound Medical, which develops and markets incision-free ablation therapies that treat diseased tissue, made the announcement on May 14.
This marks the company’s second approval related to its TULSA—Transurethral Ultrasound Ablation—AI module. Contouring Assistant is to be used alongside Profound’s TULSA PRO system, which surgeons can use to plan ablation procedures of the prostate.
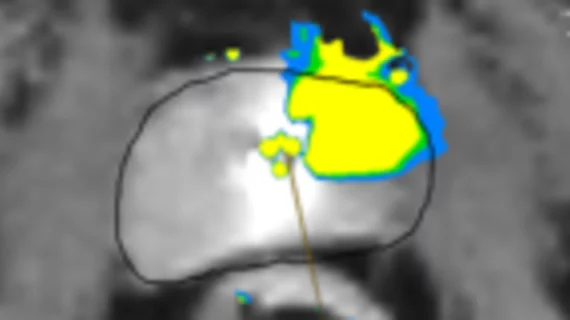
The new module is a machine learning-based segmentation tool that further enhances procedural planning. It uses more than 24 million parameters that were extracted from 7,466 training images.
After analyzing a patient’s imaging, it utilizes prior physician-created TULSA treatment designs to provide surgeons with detailed information on which design would be most effective in targeting cancerous tissue for that specific patient. As the number of completed procedures utilizing the module continues to grow, the design options providers can choose from will as well.
In clinical trials, not only was Contouring Assistant’s contouring accuracy in line with that of seasoned radiologists, but it also reduced procedure times by nearly 30%.
In a release on the approval, Preston Sprenkle, MD, a prominent urologist with Yale School of Medicine, who assisted with one of the studies, praised the product for this feature.
“Profound is to be commended for supporting this rigorous clinical analysis of the Contouring Assistant feature, which was on par with that normally associated with testing diagnostic-level AI software,” Sprenkle said. “Importantly, Contour Assistant not only allowed my esteemed urologist colleagues and I to approach the accuracy of an expert radiologist reader in our TULSA treatment designs, but also enabled us to reduce overall procedure times by one-third.”
The TULSA procedure is conducted under MR guidance. It is both incision- and radiation-free and targets cancerous tissue while also limiting the side effects associated with traditional prostate cancer treatments, like urinary incontinence and sexual dysfunction.
Profound is currently working on a third TULSA AI module. More information on that is expected to be released sometime this year.