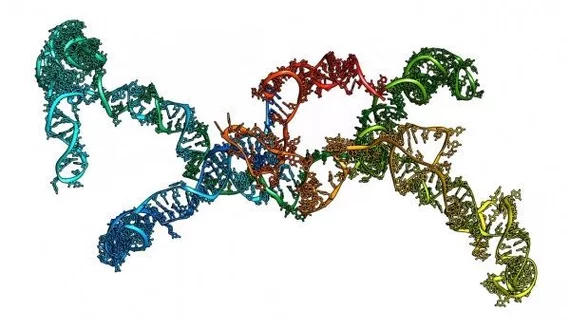
Researchers create first 3D image of heart RNA structure
The first fully three-dimensional images of special heart RNA molecules have been published Jan. 9 in Nature Communications.
Scientists from New Mexico-based Los Alamos National Laboratory believe their work could pave the way for new strategies in regenerative medicine for heart conditions.
“As far as we know this is the first full 3D structural study of any long, non-coding RNA other than a partial structure,” Karissa Y. Sanbonmatsu, with the lab’s theoretical biology and biophysics group said in a statement. “A better understanding of these RNAs could lead to new strategies in regenerative medicine for people with heart conditions due to cardiovascular disease or aging.”
Using small angle x-ray scattering, the group was able to uncover the 3D "envelope" of the RNA molecule critical for programming stem cells. And with the help of machine learning and advanced computing, the researchers created atom-level models to fit inside these envelopes—the longest isolated RNA model currently available.
Prior to 2000, when the human genome was sequenced, most experts believed it consisted mainly of instructions for proteins. However, it has been proven that 90% of the genome encodes a new class of RNA molecules to help control which genes are turned on and off. Malfunctions in this process, for example, can cause birth defects, autism and even cancer.
“Our work represents the first step in showing that these difficult-to-image RNAs do possess 3D structures, and that these molecular structures may very well determine how they operate,” Sanbonmatsu added. “The RNA studied is called ‘braveheart’– it triggers the transformation of stem cells into heart cells.”