Deep learning predicts pneumonia mortality on chest X-rays
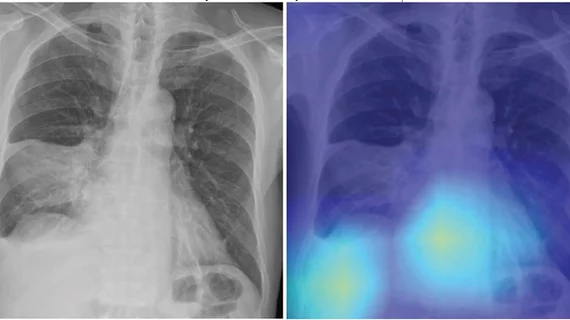
Chest radiography is an essential tool for diagnosing community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), although it has an uncertain prognostic value. But according to an accepted manuscript published in American Roentgen Ray Society's (ARRS) American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a deep learning-based model using the initial chest X-rays accurately predicted 30-day mortality [1]. The researchers said this improves upon the performance of an established risk prediction tool, the CURB-65 score.
“The deep learning (DL) model may guide clinical decision-making in the management of patients with CAP by identifying high-risk patients who warrant hospitalization and intensive treatment,” concluded first author Eui Jin Hwang, MD, PhD, from the department of radiology at Seoul National University College of Medicine in Korea.
In this manuscript, a DL model was developed in 7,105 patients at one institution from March 2013 to December 2019 to train, valid and for internal test sets to predict risk of all-cause mortality within 30 days after CAP diagnosis using patients’ initial chest radiograph. Hwang et al. then evaluated their DL model in 947 patients diagnosed with CAP during emergency department visits at the same institution as the development cohort from January 2020 to December 2020, and 848 additional patients from two other institutions between January 2020 to December 2020 and March 2019 to October 2021. The study compared between the artificial intelligence DL model and a risk score based on confusion, blood urea nitrogen level, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and age ≥ 65 years.
Ultimately, a DL model using initial chest radiographs predicted 30-day, all-cause mortality in patients with CAP with an area under the curve (AUC) ranging from 0.77 to 0.80 in test cohorts from the different institutions. Additionally, the model showed higher specificity (range, 61–69%) than the CURB-65 score (44–58%) at the same sensitivity, the authors wrote.
Hwang said the clinical impact is that the deep learning-based model may better guide clinical decision-making in management of patients with CAP.