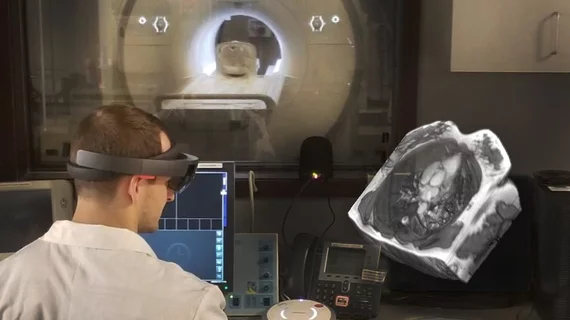
Microsoft, Case Western to explore 'fingerprinting' to improve MRI accuracy
Microsoft will collaborate with Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) in Cleveland to improve the accuracy of MRI results in less time through an approach called "magnetic resonance fingerprinting."
The process, which will combine Microsoft's quantum-inspired algorithms and machine learning, utilizes a varying sequence of pulses to produce a single unified diagnostic exam, according a May 18 blog post by Todd Holmdahl, MSE, corporate vice president of Microsoft Quantum.
Final quantitative maps are generated by comparing the response against a lookup table that produces a quicker characterization of tissues, Holmdahl wrote.
To ensure the approach produces efficient MRIs, Microsoft plans to optimize the pulse sequences by mapping the problem in an acceptable format for quantum computers and then use their quantum–inspired algorithms to complete the scan.
Once the MRI is complete, Microsoft HoloLens will be used to create a 3D, holographic model of the results, according to Holmdahl.
"By generating an optimized pulse sequence, researchers at CWRU will be able to create a solution that improves the diagnostic capability of MRI," Holmdahl wrote. "This work will lead to an improved patient experience, requiring less time in the MRI machine and providing more accurate, rapid results."