AI tool accurately completes leg length measurements up to 87% faster than human readers
Artificial intelligence-assisted leg measurements are as accurate as those taken manually by radiologists, but they take just a fraction of the amount of time to complete.
In fact, the AI-assisted measurements are completed nearly 90% faster than manual measurements on average, according to new data published in the journal Clinical Imaging.
Leg length discrepancies (LLDs)—when the lower extremities are two different lengths—are common, but when the difference in leg length is significant, it can lead to painful and sometimes disabling complications, like osteoarthritis, hip pain, knee pain, low back pain, scoliosis, and altered gait patterns.
Some individuals with LLD are candidates for surgical correction; it is imperative that the measurements obtained to guide such surgeries are accurate. However, there are issues with completing these measurements manually, as it is a time-consuming process, and its reproducibility is challenging.
This is a task in which AI can be especially beneficial, authors of the new paper indicated.
“Due to AI's automated nature, it typically produces results much faster than its human counterparts and without causing a fatigue factor,” corresponding author Avneesh Chhabra , from University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, and colleagues suggested. “In addition, if successfully validated, the measurements can be provided in remote settings where a specialist radiologist's availability is limited.”
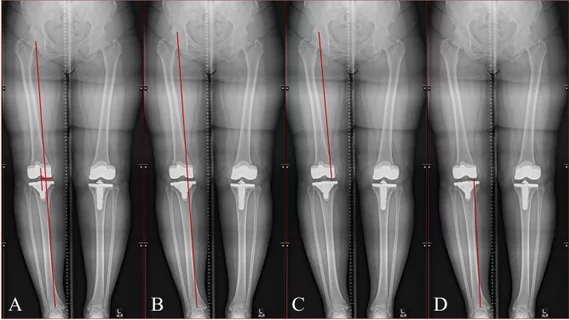
To compare AI-assisted measurements to those completed by radiologists, the team tested an AI software with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s 510(k) clearance (IB Lab LAMA, IB Lab GmbH, Vienna, Austria) on the imaging of 320 lower extremities. Multiple measurements of the entire extremity were taken and assessed using intraclass correlation coefficients and Bland-Altman analysis.
The AI tool consistently achieved results in the excellent range for between 9-12 out of 13 different variables. Its accuracy was greater for leg measurements than for angular measurements, but its overall performance was comparable to that of three human readers, with one exception—time.
Readers recorded assessment times of 250, 282 and 236 seconds, while the AI tool tool required just 38 seconds on average.
“Although it is well-known that AI can save time, it is useful to see the magnitude of time that can be saved specifically in radiographic evaluation of the lower extremity,” the group noted. “Clinicians could take advantage of the time saved by using AI on this repetitive, standardizable task and spend more time on more complex tasks such as preoperative assessment and planning.”
The experts suggested that their results signal that the tool utilized in this study (and other similar tools that may be developed) could be a viable option for standardizing leg length and angular measurements in the future.
The study abstract is available here.