DL model's pancreatic lesion detection in line with that of board-certified radiologists
A deep learning-based approach to identifying pancreatic lesions on CT imaging was recently shown to perform in line with radiologists.
The model was validated on multiple test sets after being trained on CT imaging data from nearly 900 patients—one set with abnormal imaging that warranted resection for pancreatic lesions between January 2014 and March 2015, and another set without pancreatic abnormalities on imaging.
The results of the research are published in Radiology, where co-senior author of the study Hyoung Jung Kim, of the Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, and colleagues discussed the utility of deploying artificial intelligence to analyze imaging pancreatic lesions.
“The diagnostic performance for detecting pancreatic lesions at CT largely depends on the level of experience of the radiologist,” the authors wrote. “At the same time, the growing number and complexity of imaging examinations have expanded the workload and pressure on radiologists to read more studies in shorter periods, thus leaving them susceptible to diagnostic errors.”
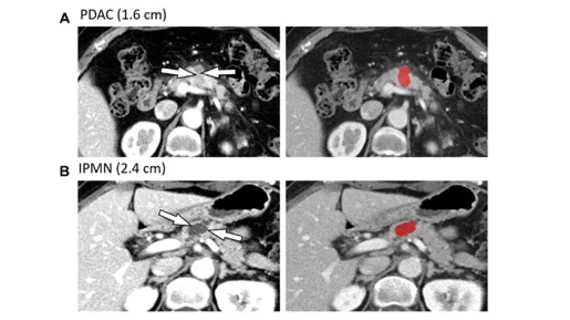
For the study, the deep learning model was evaluated on two test sets—one temporally independent cohort (test set 1) and a temporally and spatially independent cohort (test set 2). The model’s performance was measured against two board-certified radiologists.
Using the first test set, the DL model achieved an AUC of .91; for the second test set, the AUC was slightly lower at .87. The model had high sensitivity for solid lesions of varying sizes (98%-100%) and for cystic lesions measuring 1 cm or larger (92%-93%). Both measures were comparable with the performances of the radiologists.
Experts involved in the study suggested that these findings indicate that DL has the potential to play a supportive role to radiologists who are assessing pancreatic lesions.
“Our approach has the potential to facilitate timely diagnoses and management of pancreatic lesions encountered in routine clinical practice,” the authors concluded.
The study abstract can be viewed here.