Imaging Contrast
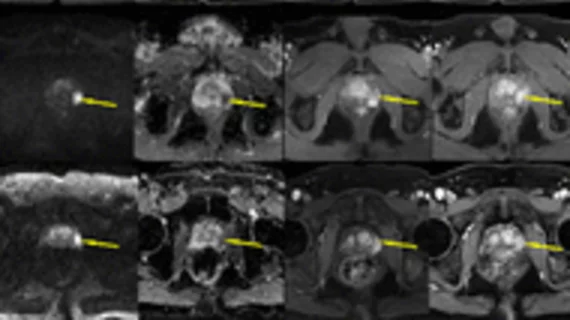
Contrast agents are injected into patients to help enhance images to make it easier for radiologists distinguish specific areas of the body from surrounding tissues. The most commonly used agents are iodinated contrast dye for computed tomography (CT), interventional cath lab angiography, RF fluoroscopy, and in surgical OR procedures. MRI scans typically use gadolinium-based contrast agents. Ultrasound and echocardiography (cardiac ultrasound) imaging use contrast agents composed of microscopic bubbles to enhance images that otherwise would be suboptimal.