NorthStar teaming up with cancer therapy leader to bolster global radioisotope supply
Nuclear medicine firm NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes is partnering with cancer treatment developer Ion Beam Applications to increase the world’s access to technetium-99m, the pair announced Monday.
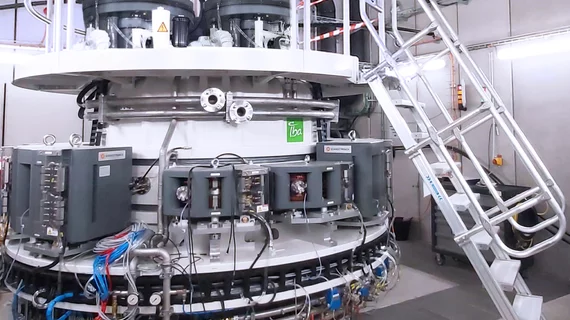
The agreement builds upon an existing contract under which IBA provides NorthStar with a maximum of eight electron beam accelerators to help produce non-uranium-based Mo-99—used to generate the Tc-99m radioisotope. And as a result of this new collaboration, organizations outside the U.S. will have access to NorthStar’s proprietary Tc-99m Generation Systems.
“Every year approximately 30 million patients benefit from diagnostic imaging studies using Tc-99m,” Stephen Merrick, president and CEO of the Beloit, Wisconsin-based nuclear imaging company said in a statement. “NorthStar is delighted to expand its collaboration with IBA, as we view them to be an ideal partner to grow the use of non-uranium-based Mo-99 to support a sustainable and innovative future for nuclear medicine.”
The first pair of IBA accelerators for NorthStar's Accelerator Production facility is set to arrive from Belgium early next month, according to the announcement.
In other company news, NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes last week announced a reorganization effort it said would further enhance the availability of Mo-99 and advance additional radioisotopes currently under development.
Its first move was to appoint Dave Wilson as vice president of the company’s Advanced Radiopharmaceutical and Therapeutic Technologies business. With five years of experience at the organization, Wilson will help develop the radioisotopes copper-67, actinium-225, and FibroScint (technetium-99m F4A).