X-ray markers may skew AI's ability to interpret extremity radiographs
Although artificial intelligence offers numerous advantages, new research published in the American Journal of Roentgenology has unearthed new roadblocks for interpreting certain images.
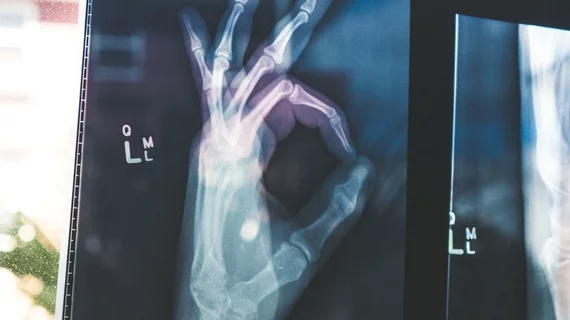
“Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained to diagnose abnormalities on bone radiographs often focus on laterality and/or technologist initial labels to indirectly make predictions,” Paul H. Yi, MD and co-authors explained. X-ray markers may skew this ability, they added, when using AI to automatically recognize abnormalities.
The retrospective study evaluated 40,561 upper extremity radiographs used to train CNN classifiers. Three inputs were used to differentiate between normal and abnormal images: 1). original images with anatomy and markers; 2). images with tech initials subsequently covered by a black box; and 3). radiographs in which boney anatomy had been removed and only the X-ray markers remained.
The AUC for the original images with tech markers and anatomy was 0.84. Covering the markers yielded an increased AUC of .86 with heatmaps tending to redirect towards the bone, rather than the X-ray markers. When the anatomy was removed from images and the labels alone were evaluated, the AUC decreased to .64. Authors note that this indicates some labels could be more connected with anomalies than others.
Since technologists are required to include image annotations to orient anatomy and positioning, researchers note that future development CNNs should take this into consideration.
“Our results demonstrate that CNNs trained to diagnose abnormalities on bone radiographs often focus on laterality and/or technologist initial labels to indirectly make predictions,” authors noted. “We recommend that such potential image confounders be collected when possible during dataset curation, and that covering these labels be considered during CNN training.”
You can read the full study in The American Journal of Roentgenology.