Cardiac Imaging
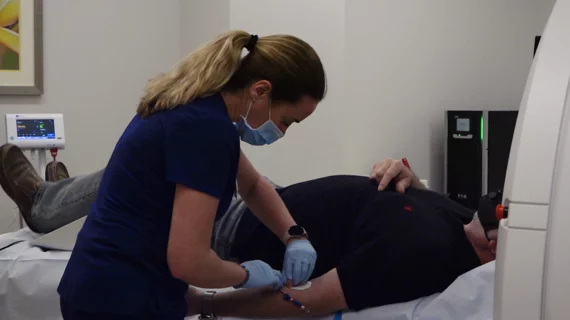
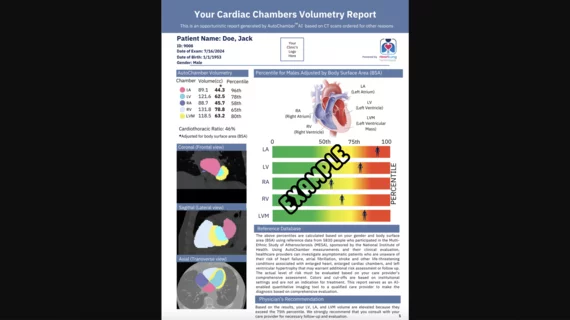
While cardiac ultrasound is the widely used imaging modality for heart assessments, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear imaging are also used and are often complimentary, each offering specific details about the heart other modalities cannot. For this reason the clinical question being asked often determines the imaging test that will be used.
Displaying 1537 - 1544 of 1765