Ultrafast MRI protocol reduces scan time by 10 minutes for cervical imaging
Deep learning-based reconstruction of cervical spine imaging could shorten the amount of time required to obtain cervical MRI exams without sacrificing diagnostic value.
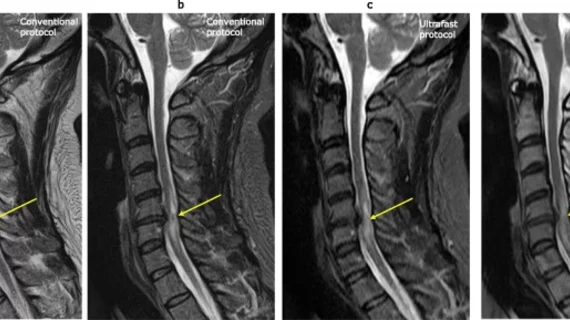
That’s according to a recent study published in the European Journal of Radiology, where experts compared standard cervical MRI protocols to those using a deep learning-based reconstruction (DLR) technique. The ultrafast protocol was able to reduce acquisition times by around ten minutes [1]—a feat that experts involved in the study suggested could open doors leading to greater utilization of MRI in the future.
Although MRI is an ideal imaging modality to assess various conditions of the cervical spine, corresponding author of the new paper, Nobuo Kashiwagi, with the Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at Osaka International Cancer Institute, and colleagues explain that its use is limited due to its often-lengthy acquisition times.
“The inherent trade-off relationship between MRI acquisition time and spatial resolution or signal-to-noise ratio results in a long acquisition time, as compared with other modalities, thereby limiting the clinical utility of MRI in motion-prone patients due to pain, patients with time-critical disease, and pediatric patients who require sedation,” the authors wrote.
Researchers tested the DLR technique on 50 patients who underwent cervical spine MRI using both conventional and ultrafast protocols. Using the DLR technique, acquisition times dropped from 12 minutes and 54 second to 2 minutes and 57 seconds. Experts shared that not only did the technique significantly shorten scan times, it also yielded nearly equivalent diagnostic results compared to conventional protocols and “almost perfect” inter-protocol intra-reader agreement for all variables.
The experts indicated that the ultrafast protocol could have a future role in the imaging of patients who struggle to complete MRI exams due to the positioning-related pain or difficulty holding still for extended periods of time, especially for children.
The study abstract can be viewed here.