Magnetic Resonance Imaging
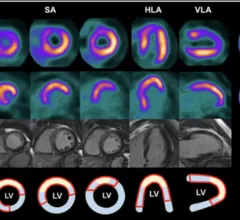
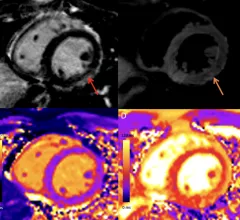
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging MRI is used as both a functional and anatomical cardiac imaging test. It offers excellent soft tissue detail and the ability to quantify cardiac function. MRI scans can be performed with or without gadolinium contrast depending on what information is needed. Unlike computed tomography (CT), MRI does not use X-ray radiation, but patients with metal implants may have contraindications for MRI use because MR will heat up most metal objects. MRI exams usually take much longer than CT scans. How does MRI work? MR creates images by using powerful magnets to polarize hydrogen atoms in water (the body is made of of more than 80% water) so they face in one direction. A radiofrequency pulse is then used to ping these atoms, causing them to wobble, or resonate. The MRI coils detect this and computers can assemble images from the signals. Basic MRI scans will focus on the resonance of fat and water in two different sequences, which highlight and contrast different features in the anatomy.
![The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) has shared new recommendations for performing medical imaging exams on heart failure patients with surgically implanted left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) and temporary mechanical circulatory support (TMCS) devices. The guideline, published in full in the Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography, represents ASE’s first update on the topic since 2015.[1]](/sites/default/files/styles/top_stories/public/2024-09/screenshot_2024-09-10_at_2.06.47_pm_0.png.webp?itok=JY7Oyzce)