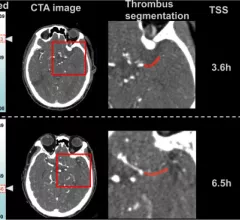
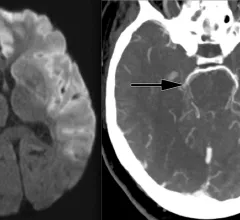
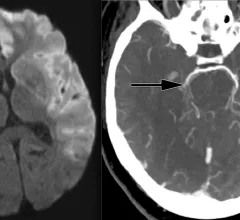
Stroke
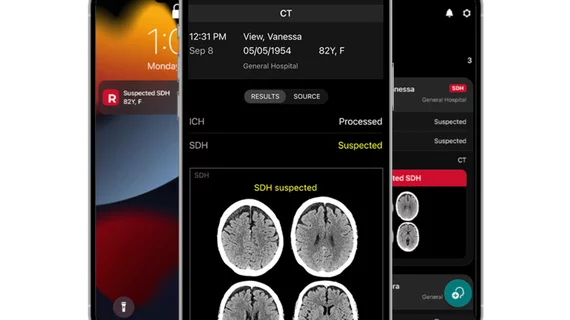
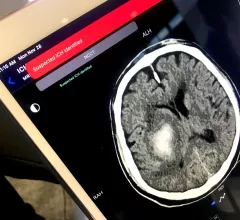
Cardiovascular departments are playing a role in stroke interventions at numerous health systems, working as part of the stroke care team with neurologists, radiology and the emergency department. Stroke first has be be classified as ischemic or hemorrhagic. These have very different care pathways. Ischemic strokes are increasingly being treated with neurological-interventional therapy that includes catheter based mechanical thrombectomy to remove the clot. This is a more aggressive treatment compared to traditional IV administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) thrombolytic therapy to dissolve the clot. Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) and intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) brain bleeds can also be treated in some cases stent flow diverters and embolization coils.