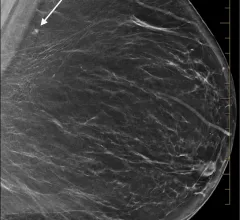
Connie Lehman, MD, PhD, chief of breast imaging, co-director of the Avon Comprehensive Breast Evaluation Center at the Massachusetts General Hospital, discusses the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic on breast screenings, increased cancer rates and issues with the vaccines causing false positives on mammograms.