Computed Tomography
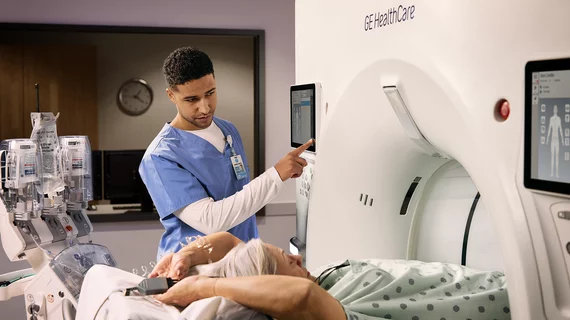
Computed tomography (CT) is a fast and accurate imaging modality often used in emergency settings and trauma imaging. CT scans, with or without (or both) iodinated contrast are frequently used to image the brain, chest, abdomen and pelvis, but also have post-imaging reconstructive capabilities for detailed orthopedic imaging. It is now a standard imaging modality in emergency rooms to quickly assess patients. CT uses a series of X-ray images shot as the gantry rotates around the patient. Computer technology assembles these into into a dataset volume than can be slices on any access, or advanced visualization software can extract specific parts of the anatomy for study. Find more content specific to cardiac CT.