Breast Imaging
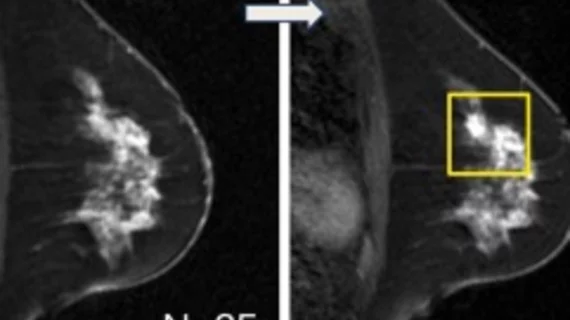
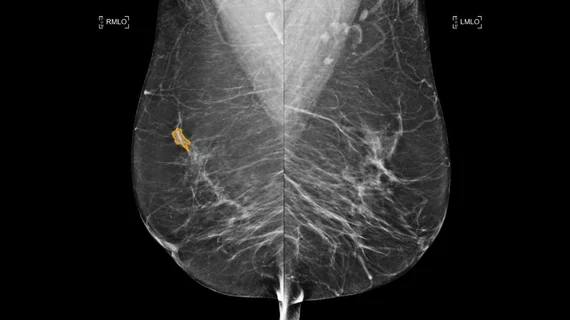
Breast imaging includes imaging modalities used for breast cancer screenings and planning therapy once cancer is detected. Mammography is the primary modality used. Mammogram technology is moving from 2D full-field digital mammography (FFDM) to breast tomosynthesis, or 3D mammography, which helps reduce false positive exams by allowing radiologists to look through the layers of tissue. Overlapping areas of dense breast tissue on 2D mammograms appear similar to cancers and 3D tomo helps determine if suspect areas are cancer or not. About 50% of women have dense breast tissue, which appears white on mammograms, the same as cancers, making diagnosis difficult. Radiologists use the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) scoring system to define the density of breast tissue. Many states now require patients to be notified if they have dense breasts so they understand their mammograms might be suboptimal and they should use supplemental imaging that can see through the dense areas. This includes tomosythesis, breast ultrasound, automated breast ultrasound (ABUS), breast MRI, contrast enhanced mammography and nuclear imaging, including positron emission mammography (PEM).